-
Make your “ChatGPT” and other GenAI expectations clear
Links and terminology were updated October 2023 Students want to know what your expectations are. Sometimes students feel uncertain about what to ask or how to ask. Students learn quickly that different instructors, in different programs, handle and regard some things differently when it comes to rules for academic integrity. The reasons for this can relate to discipline, to learning outcomes, to assessment type, and to the philosophy of the educator. The syllabus and any information posted alongside assessment details are excellent “placements” of clear expectations. Here are some pointers and resources: A link to the USask syllabus information suggested language related to permitted or unpermitted use of…
-
10 Guidelines for Assessment Practice in a GenAI Environment
This post was updated for links and terminology in October 2023. Generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) tools, such as but not limited to ChatGPT, are increasingly available with quickly advancing capabilities. Proper and ethical use is important for transparent and valid assessment. The following are 10 general guidelines for educators. To prepare Learn about relevant, new GenAI technologies and their applications in contexts of interest. Discuss approaches and emerging practices with disciplinary colleagues. Design assessment to meet course learning outcomes in ways that include acceptable uses of GenAI tools and/or reduces the likelihood of unacceptable uses. During the course Explain how students should and should not complete their assessments and…
-
Comparing two online quizzes: Formative Assessment
This post aims to compare the design of two online quizzes to determine how each design impacts student learning. Formative assessment is a process used to: Identify what students already know and where they need more support to reach the desired learning outcomes. Provide feedback that the student can use to increase learning before a final assessment. For example, using feedback from a draft assignment that can be used to increase understanding for future revisions. Evaluate the effectiveness of the instruction during the learning process so the teacher can adjust instruction to meet students’ needs. “You almost want kids to make mistakes on formative assessments because that’s how you figure out…
-
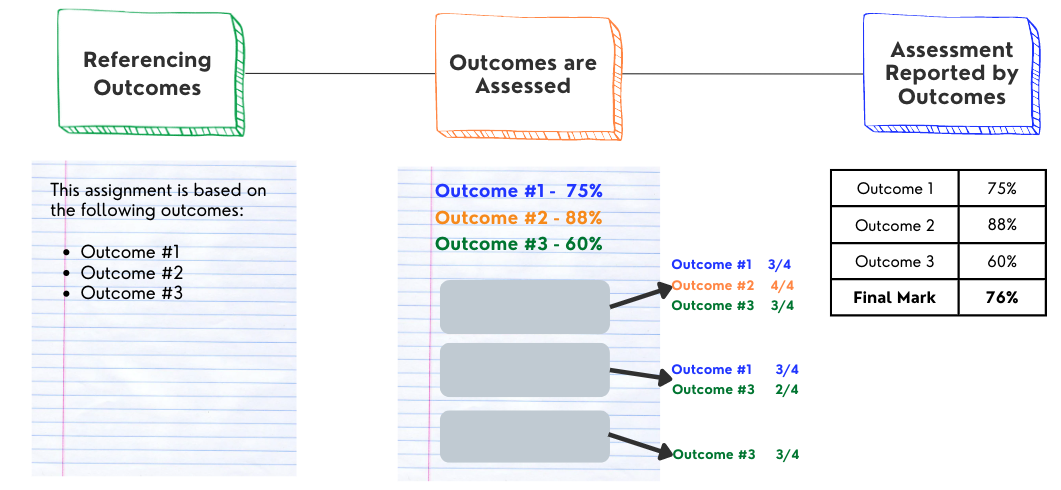
An Outcomes-Based Practice Continuum
This article will discuss a continuum of outcomes-based practices including referencing outcomes, assessing outcomes, and reporting student achievement on outcomes. Referencing Outcomes Referencing outcomes is a beginning outcomes-based practice. Outcomes are referenced within each assignment, often with the instruction section. Here, the instructor has created the assignment with the outcomes in mind and makes this visible. However, outcomes are not assessed separately, and assignments are given a ‘blanket score’ for multiple learning outcomes. Gradebook reporting is done by assignment. Assessing Outcomes within Assignments The next stage occurs when the outcomes within assignments are assessed. This stage provides valuable insight to determine the most important areas for improvement. Instructors create valid tools,…
-
Will you allow ChatGPT? Considerations.
Many instructors are surprised by the capabilities of a new artificial intelligence text generator – ChatGPT – that was released in November, 2022. Try it out . Many are asking what the right thing to do is in terms of allowing or disallowing its use. In the short-term, it is reasonable to be contemplating whether to “ban” use of ChatGPT for course assessments. In the long-term, these tools will become even better and more pervasive and our assessment practices will surely need to change. In fact, opportunities to incorporate this tool and those like them are set to inspire all kinds of exciting changes in higher education and the world…
-
ChatGPT and Academic Misconduct Regulations
What is ChatGPT? ChatGPT is an generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) text generator that has been trained on data sets of mind-boggling size. It produces apparently “original” and coherent text responses in what is referred to as natural language. Tools of this kind have been in use in a range of sectors and have been on the radar of writing, technology, and academic integrity experts for at least two years. The ChatGPT functionality and its open availability have leapt ahead in public awareness and reaction since November 30, 2022. If you haven’t yet heard about ChatGPT, to find out more and to try it, go here. Experiment with the tool, including putting…
-
Assessing Outcomes versus Grading Assignments
Shift your focus from grading tasks to assessing outcomes. Learn how this approach fosters deeper learning and provides a more meaningful evaluation of student progress. In this article, we will examine why assessing outcomes can target learning improvements better than grading assignments.Ooutcomes-based assessment starts with articulating what students will be able to do (the learning outcomes), followed by designing learning activities and assessments linked to the outcomes. However, even with clear outcomes and learning activities, instructors often fall into the habit of grading assignments rather than assessing outcomes. Consider the following scenario. Learner 1 and Learner 2 both have 75% in your class. How do you, the instructor, or the…
-
Creating Efficiencies: Grading Discussions in Canvas
Perhaps you are using Discussions in Canvas as a supplement to your face-to-face class or using it in an online course. While students’ posts may provide evidence of their learning and allow for online engagement, giving feedback on the posts is a vital part of the process – and as you are no doubt aware, can be a very time-consuming task! Strategies to manage your marking load and provide timely, actionable, and specific feedback for students, seem to fall into three categories: 1) Lighten the load for everyone: Requiring weekly discussions may impact quality through posting and grading burnout; consider bi-weekly discussions or the option for students to post…
-
Assessment Design and Academic Misconduct
First, the not-so-good news There is no such thing as a “cheat-proof” assessment. Now, for the good news Instructors can reduce the likelihood of academic misconduct through assessment design and the context for assessment. Such designs and contexts are those that help students to see the value of the learning, hold positive expectations, and regard academic integrity as the norm. We can categorize these in terms of actions to take related to assessment method, nature of the restrictions or conditions set for completing the assessment, and context for the learning itself. The following table groups strategies and what we might expect students to say (in italics) about the…
-
How Canvas Supports Learner-Centred Assessment
By Roberta Campbell-Chudoba This post is part of a series about using Canvas to integrate the eight Learning Technology Ecosystem Principles. In this post, we look at the Inclusive of learning-centred assessment principle. Inclusive of learning-centred assessment: Learning and feedback are iterative, and assessment comes from multiple sources, including self, peers, teachers, and outside experts. Effective assessment practices follow from a learner-centred teaching approach, with practices designed to produce evidence of the kind of learning you want to measure, aligned with the learning outcomes for the course. Feedback needs to be both affirming and corrective in order for any of us to learn, and if it is unambiguous, specific, frequent, and…